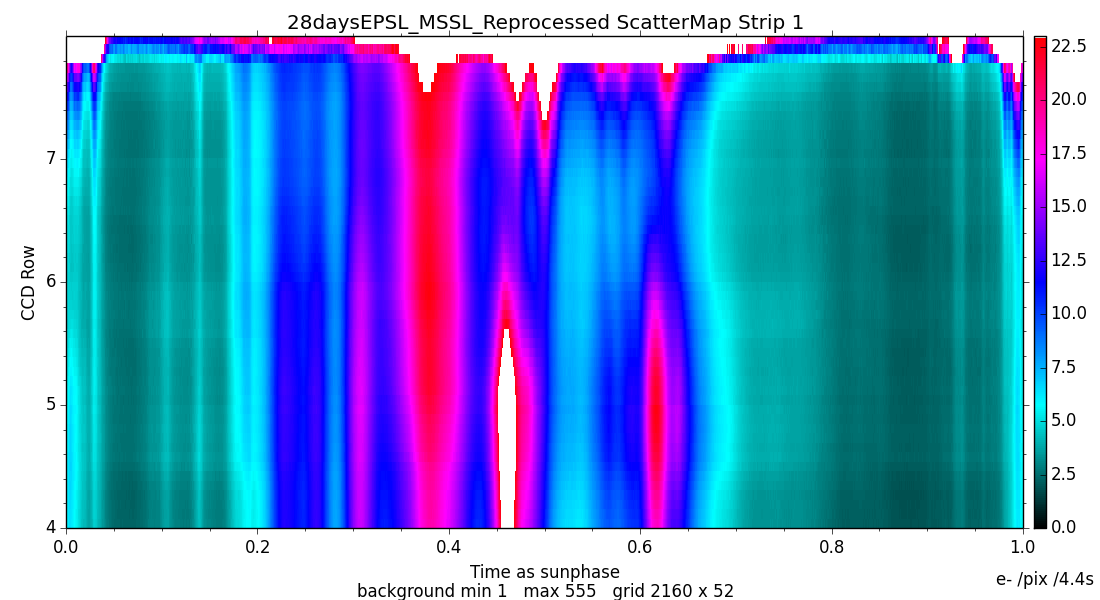
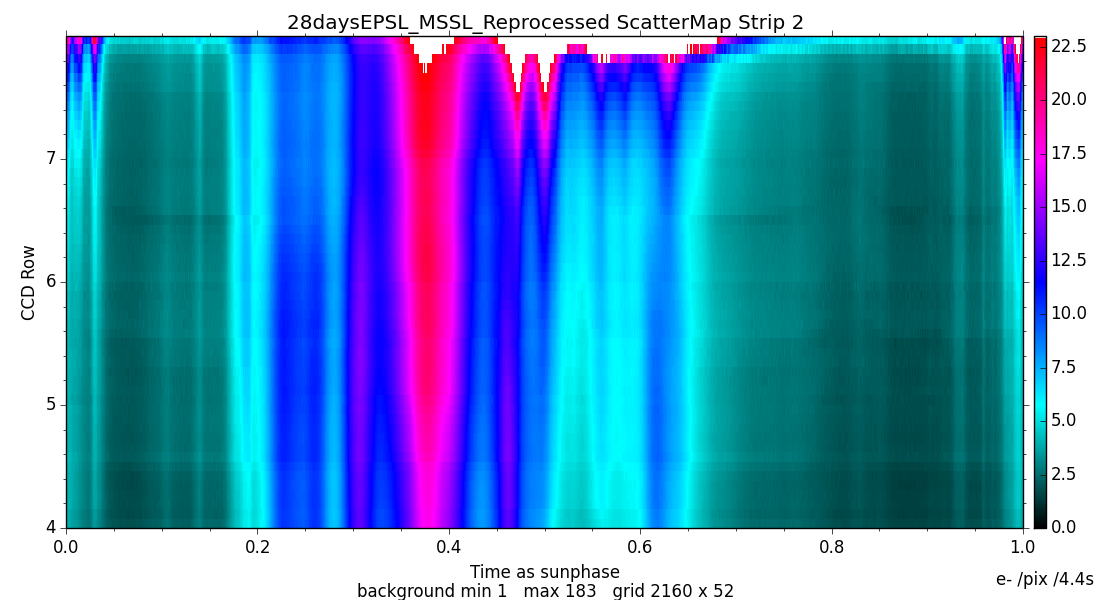
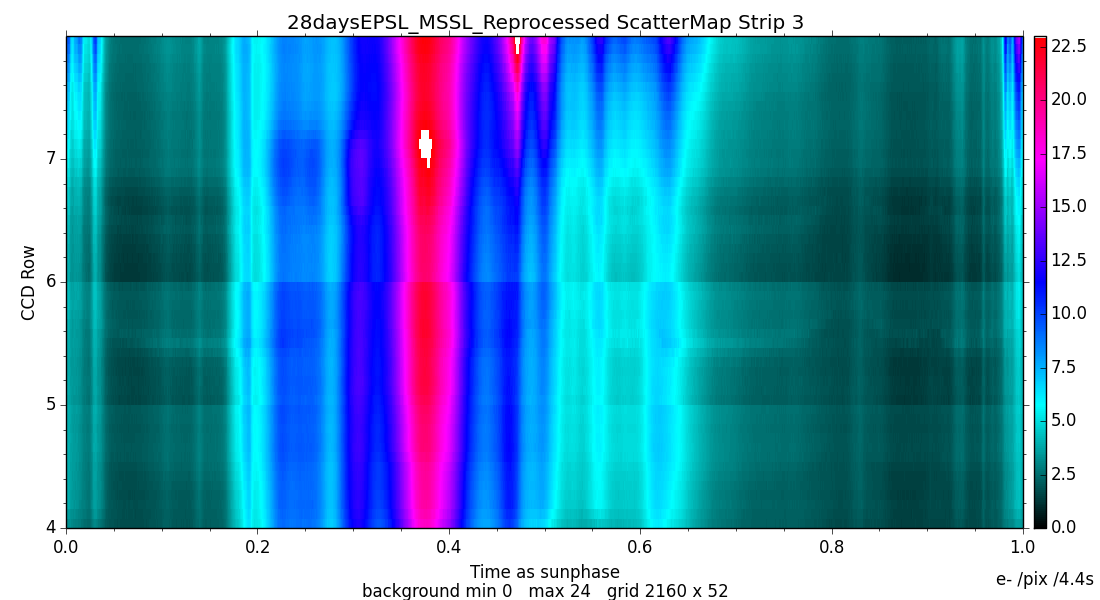
6.3.3 Straylight background
The RVS straylight background (Section 1.3.3) is measured using virtual objects (VOs; Section 1.1.3) as described in Cropper et al. (2018), Sartoretti et al. (2018)). All the RVS VOs from the first month of the mission (28 days Ecliptic Pole Scanning Law) were processed off-line. The median flux value of each VO, which contains 1260 samples, was computed, to avoid contamination by cosmic rays and stellar spectra. The row fraction coordinate (out of RVS CCD rows 4-7) and heliotropic spin phase were also calculated. All the virtual objects belonging to the same cell are combined to obtain a median value, removing outliers. A straylight map (see Figure 6.3) was constructed for each of the three RVS CCD strips (Figure 1.2) using a grid of 2160 cells in the spin direction and 50 cells in the AC direction covering the four RVS CCD rows. This map is used to correct all the Gaia DR2 data, neglecting any temporal variation.